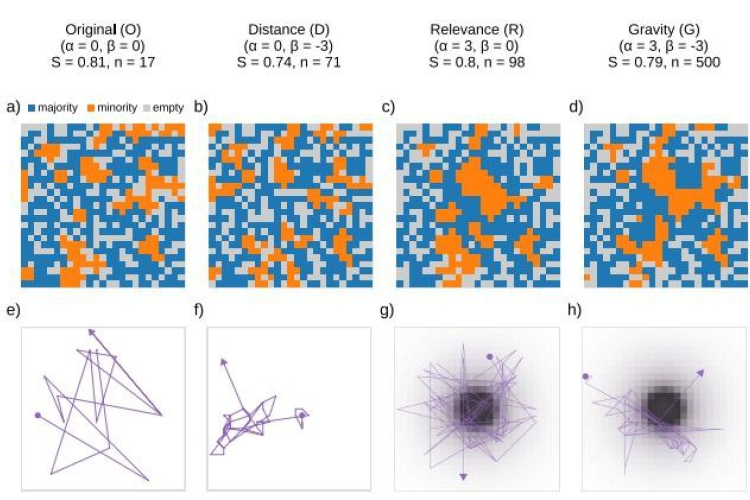
Segregation of people in urban contexts, i.e., the trend that people have to aggregate or separate into groups according to the presence or the lack of similar people, is a long-studied phenomenon. In fact, understanding urban segregation is crucial for policymakers to prevent negative social consequences such as limited access to quality education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.
Cryptocurrencies have the potential to revolutionize the world of finance, providing individuals with more freedom and trustless services. However, this new paradigm also comes with high risks for inexperienced users.
From a TNA experience.
Author: Shakshi Sharma, Host Organization: University of Sheffield, UK. Mu University: University of Tartu, Estonia.
By Simona Re (ELI), Angelo Facchini (IMT), Daniele Fadda (CNR-ISTI)
In this era of global climate and ecological crisis, rethinking our relationship with nature and developing a sustainable and innovative management of natural resources can play a critical role in ensuring both nature conservation and the well-being of citizens.
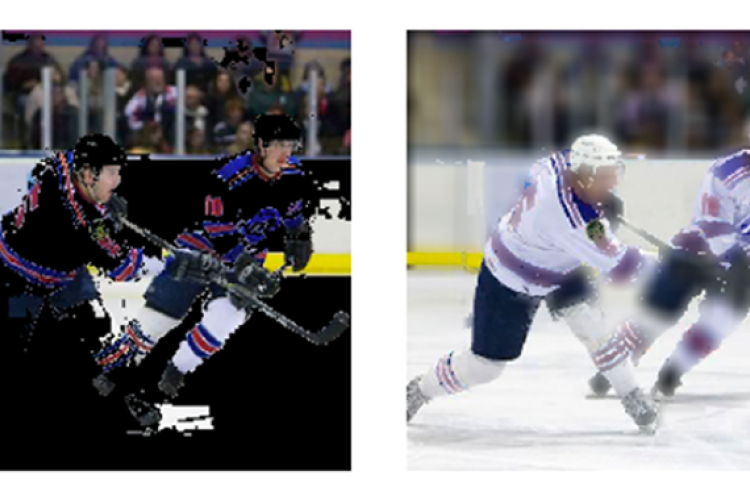

Explainable AI (XAI) has gained popularity in recent years, with new theoretical approaches and libraries providing computationally efficient explanation algorithms being proposed on a daily basis. Given the increasing number of algorithms, as well as the lack of standardized evaluation metrics, it is difficult to assess the quality of explanation methods quantitatively. This work proposes a benchmark for explanation methods, focusing on post-hoc methods that generate local explanations for images and tabular data.
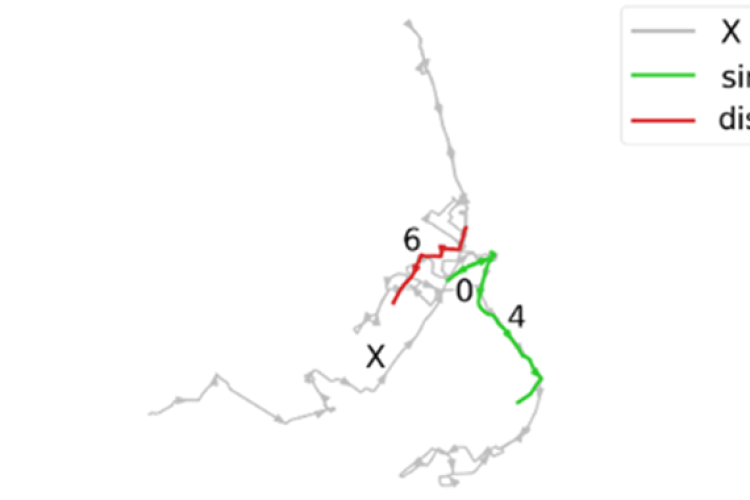
Geolet simplifies complex mobility data and outperforms black-box models in terms of accuracy while being much faster. This innovation allows for more informed decisions in various domains like traffic management and disease control, thanks to its improved interpretability.
Reminiscences from the colloquium celebrating the 10 years of the RESET scientific journal
Authored by Michele Mazza (CNR-IIT)
Revised by Guglielmo Cola and Maurizio Tesconi (CNR-IIT)
Social media platforms are abused and misused, most commonly through fake accounts, giving rise to coordinated inauthentic behaviors (CIB). Even though efforts have been made to limit their exploitation, ready-to-use fake accounts can still be found for sale in a number of underground markets. In order to study the behavior of these accounts, we developed an innovative approach to detect and track accounts for sale.
